# Uncle Bob - Robert C Martin
# Clean Architecture and Design
- privilages son of a god.
- Age of earth (opens new window)
4.5 billion years - Dianosaures are very recent, just with in a last 100 years or so.
- When did life crawl out of the oceas?
- Life began and stayed in ocean for 3.5 billion years
- How important s/w is today? How much s/w is running on your body today?
- how many processors are around you?
- Now a days its cheapers to filer out 50 cycle hums (opens new window) in speakers using s/w
- C s/w performing some fast fourier transform (opens new window)
- A modern car has 100 million lines of code running inside it.
- There is an
ifin the electric drive system of car- How many people have died because of s/w error?
- Several dozen, toyota (opens new window)
- How many people have died because of s/w error?
- Knight Capital (opens new window) lost 450 millon $ in 45 mins.
- s/w you and I write can kill people, can loose money.
- Nothing can be done in western society without interacting with s/w system.
- Volkswagen usa CEO testemony to USA congress, blame on programmer
- it was just a couple of s/w developers who did it for whatever reason
- When politicians point finger at us, adn ask how can you let 10,000 people die at a stroke?
- What our ethics are?
- What are our standars that we dont go below?
- What are the disciplines we adhere to and how do we enforce them?
- An accident yes, but not due to negligence
programmers
- 1946, How many programmers were there in the world?
- 1, Alan Turing (opens new window)
- How many programmers are there in the world today?
- could be
100 million - In 73 years we have grown from 1 to 100M, what kind of growth is that?
- definately not linear, maybe exponential. But then whats the base?
Number of programmers double every 5 years? roughly. We are already like 0.8% of the popullation
Programmers would be in a state of perpetual inexperience < 5 years
- Society depends on you.
- So its important that you learn to organize your software well
- First thing that you should see is what the s/w is supposed to do! Not the framework.
- Web is an IO device, back in 1960s we dont want to know which IO system we are using.
- In UNIX programming, we dont write to a device. Instead, we write to a abstraction
stdout
- In UNIX programming, we dont write to a device. Instead, we write to a abstraction
- The architecture of the s/w yell/scream at you its intentions, like how a church and library does.
- intent and shape of system, dependency b/w components.
Web is the Detail
- Most important books on softwares written within last 30 years
- Ivar Jacobson (opens new window) 1992 Object oriented s/w engineering
- Design Patterns
- Structure_and_Interpretation_of_Computer_Programs (opens new window)
- Use cases
User story Objects - Dont assert details far too soon
- Programmers are the detail managers, we have to deal with worst possible details
- check if a file ends with
\nor\r
- check if a file ends with
- Interactor is a business rule, 2 types of business rules
- Entity application specific business rules, which are automated.
- Applicaiotn independent, business rules which would still be used even if there are no computers, like interest calculation for a banking system
- Boundaries are Interfaces
- Only the Interactors talk to the boundaries (Interfaces), entities dont know about the outside world.
- Can you test a interactor sttingi n Atlanta sipping jin and tonic? without running the rest of the system.
- For web (delivery mechanism)
- Interactor gets data from input device (probably web button/form) and puts it into a data structure called request model.
- does not depend on anything, plain old language object
- Interactors begin to inspect it., what the interaction is supposed to be by looking at request model.
- controls the dance of entities
- Interactor then build a result model gathering all the answers in the opposite direction
- Interactor gets data from input device (probably web button/form) and puts it into a data structure called request model.
- Test your systems in parts
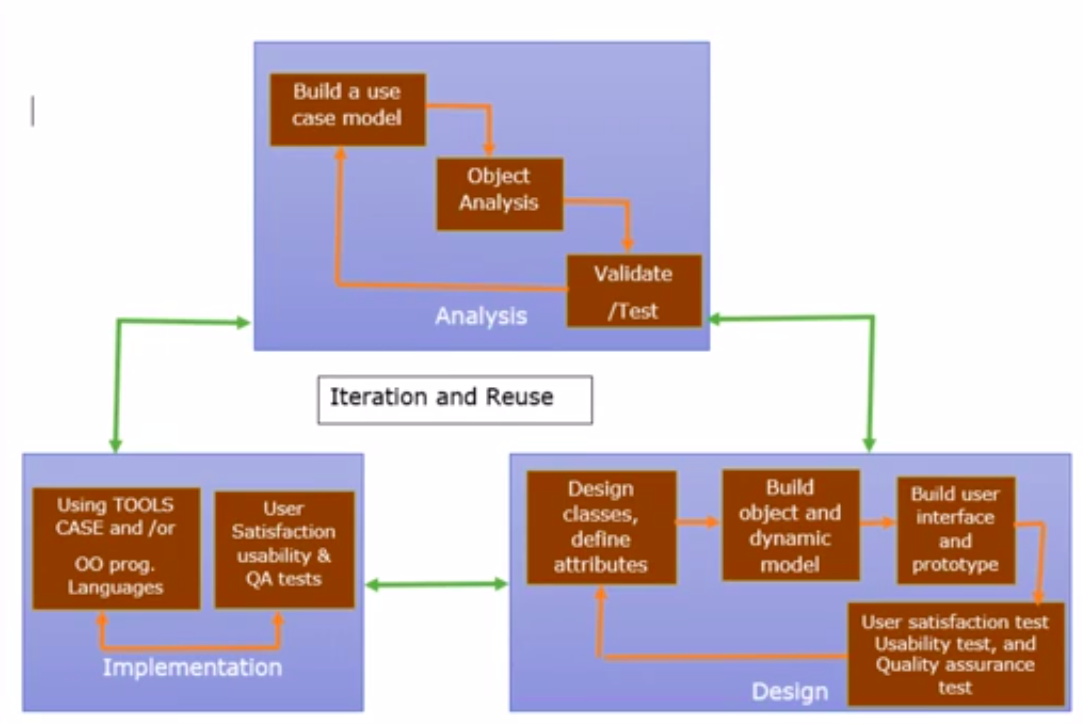
JavaandC#are same languages, microsoft stole java, earlier it was visual j++Gois one of those languages which lets you see how fast your machine really is. Unlikejavathere is no startup time. Issue execute command wait for sometime, and then bam you go.Service Oriented Architecture
Micro-services MVC pattern (opens new window)
- Model - Business rule, doesnt know how it gets its input and how it gets its output
- View - How to display contents of model to outside world
- Controller - Know how to accept input from outside world and hand it into Model
- implemented in SmallTalk
- MVC for every individual component at the small level
- MVC on web is very cluttered.
How to get data out to web? or any other IO device?
- MVC at app level could be a bad idea, no clear boundary, some controller looking code in view and model etc.
- Add a Presentor Layer reformat data in response model. as per the needs
- price as per the locale, right currency marks etc
- Any decision made about the screen is made by presentor.
Web is a plugin for Business Rules
All hail the database, all other things bow down to database because its everything.
- Wrong view, its another IO device
- Who would say that, db is the centre of everything?
- DBA's and database companies on 80s, 90s
Fitness (opens new window) java wiki tool, uncle bob wrote it with his son
- What to test and How much code coverage?
You only test the parts of the application you want to work
100% code coverage is asymptotic goal but then you never stop trying.
- GUIs are in particular harder to test
- HOw to test pixels? Testing in general over the edge of the system is hard
- How do we communicate the intent of s/w that we are developing with the s/w directory structure?
Nice to have a Use-case and entity (independent business rules) directories and promote them at the top of s/w
- Should we be using frameworks to solve our problem?
Framework authors and users have very assymetric relationship
Framework author wrote framework to solve their problem, they are not solving your problem
They love the framework, you dont! Don't couple so tightly
Over time, framework might fight you and cost you more. They are NOT pure good.
Don't overuse Dependency Injection (opens new window)
Write your code in a decoupled way, such that you can change Dependencies in future
- Inject dependencies, into a safe place behind the architectural boundary.
# SOLID Principles of Agile OO Design
- Helped push Agile manifesto
- Water is H2O, mickey mouse like structure. What holds it in place?
- Why is water good for washing? Because it can stick to dirt.
- It will dissolve everything. It has memory
- Why is water good for washing? Because it can stick to dirt.
- How does bad code slows you down?
- Coupled system - have to make changes at multiple files, propogating changes
- Fragility - once change and everything unrelated breaks
- They typed crap - spaggeti code
- Procedural Functional call Tree - every application has
- starts with main and explodes down the system
- Flow of control goes downwards
- Which of the modules knows about the other?
- Source code dependency from M
N using #importorimport - Compiler resolves these at runtime
- Source code dependency from M
High level modules knows about the low level modules. Which principle does it violate?
- Do we want out high level policy polluted by low-level detail?
- Makes code harder to read
- Why is OO part of every languague that we work on these days?
- Python is
ruby - Earlier there was no OO in
fortran,cobol. Why what happened then?
- Python is
- Objective-C in 1980's
- He was a smallTalk programmer, somebody made him porgram in C, he hated it
- He wrote a small preprocessor in front of
Cand gave it some smallTalk attributes - And then
C++came in
- Do we have encapsulation in
C?- We had perfect encapsulation.
- Forward declare functions in header file
.hand then implement them in.cfile - Objects completely screwed that up
- C++ put all the variables in header files, now all variables are visible to everyone
- implement hackey wrorks
private,public,protected,staticetc.
OO did not give us encapsulation, it weakened encapsulation. It destroyed original encapsulation (as in C) and replaced it with hackey public, protected, private, static jargons
# Inheritance
- Why doesnt java, C# have multiple Inheritance?
- java solved it by hackey Interfaces
- But we cannot inherit Interfaces - a lazy hack
- All in dynamically typed languages (python, ruby) we can have Polymorphism without Inheritance
- Inheritance is NOT necessary for polymorphism
- No Inheritance is needed for duck-types
- Inheritance in dynamic types languages is used to inherit the behaviours and variables but NOT interfaces
- With java, and C# we need inheritance to use Polymorphism
# Polymorphism
- Do we have polymorphism in C?
- Not very much, because it was dangerous as hell.
IO Driver
Every IO driver have to implement these 5 magical functions
- Read
- Write
- Open
- Close
- Seek
OS will take pointers to these functions and put them into a table
- Does java have pointers to functions?
- No, because they have polymorphism
- As soon as
C++came along, we have cheap, easy, safe Polymorphism- Module M
N calling function F
- Module M
- With Polymorphism we can do this,
- module M can mention the name of interface to use F
- module N will derievve from that interface
- Now, compile time dependency points against the flow of control, instead of with the flow of control
- You have absolute control over your dependencies by carefully deciding which direction the arrows points towards. Thats what OO is.
OO is about managing dependencies by selectively re-inverting certain key dependencies in your s/w so that you can avoid rigidity, fragility and non-reusability
Enter SOLID
- Conside selling circle, squares
jarson your website? - 1988 was a good year for principles
# Difference between DIP, IOC and DI ?
DIP in the Wild (opens new window)
DI is about how one object acquires a dependency. When a dependency is provided externally, then the system is using DI. IoC is about who initiates the call. If your code initiates a call, it is not IoC, if the container/system/library calls back into code that you provided it, is it IoC.
DIP, on the other hand, is about the level of the abstraction in the messages sent from your code to the thing it is calling. To be sure, using DI or IoC with DIP tends to be more expressive, powerful and domain-aligned, but they are about different dimensions, or forces, in an overall problem. DI is about wiring, IoC is about direction, and DIP is about shape.