# Syntax
# Loop
| loop syntax | description |
|---|---|
for ... in | loop through objects |
for ... of .forEach() | loop through array |
[1,2].map(n => n+1) | Array Methods, run a fn on each array item |
- Asynchronous Programming - Non deterministic programming
- In JavaScript, a variable can be declared after it has been used. Hoisting
- Variables defined with let and const are hoisted to the top of the block, but not initialized.
- Meaning: The block of code is aware of the variable, but it cannot be used until it has been declared.
- JavaScript only hoists declarations, not initializations.
- Difference between javascript function and assigning function to a variable?
Both are different. Source (opens new window)
var functionOne = function() { // Some code }; function functionTwo() { // Some code }- Variant #2 uses hoisting, whereas #1 would be initalized only once variable is reached and read by compiler.
- variant #1 uses anonymous function (opens new window) assigned to a variable.
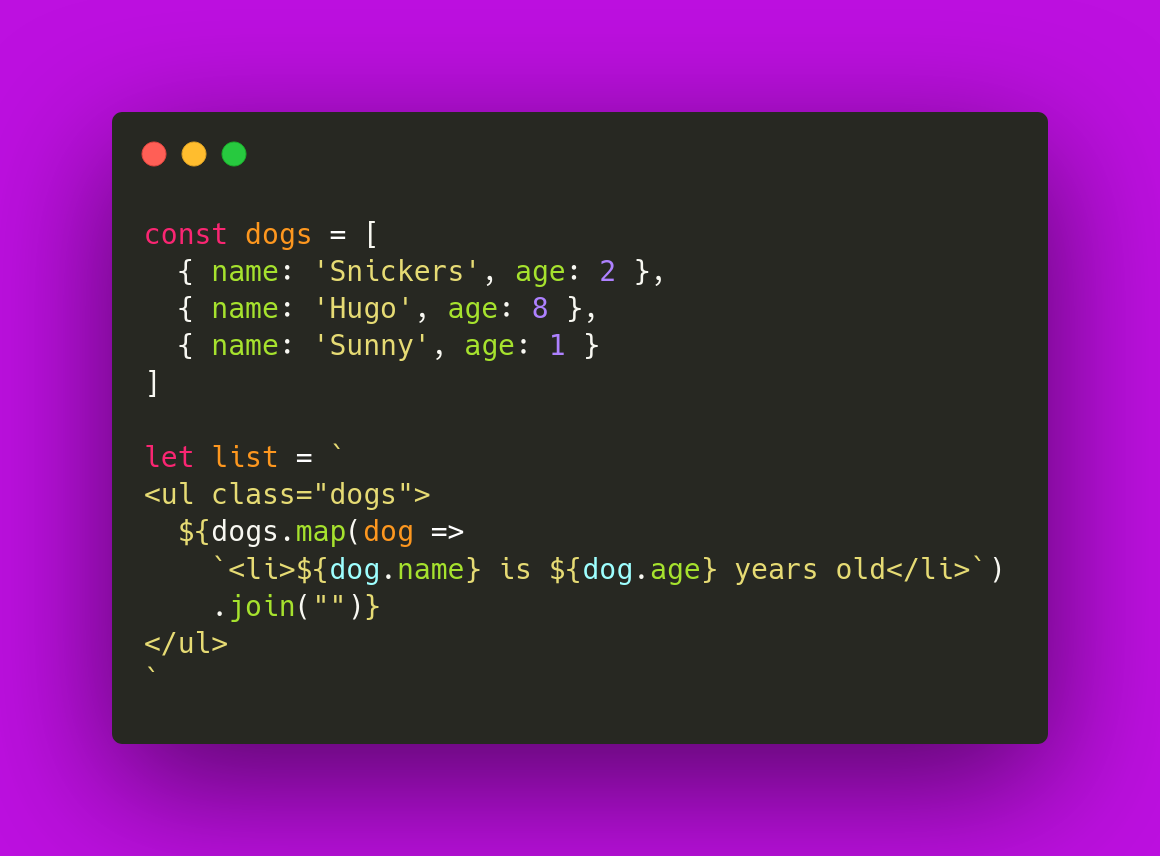
# Tagged Template Literals Use cases
- static content and dynamic content
- just tagged templated string in jest to parameterized test cases.
test.each - change data to human redable strings
2 hours ago - calculate the works in template and calculate read time count.
- Localization
- GraphQL
const fb: string = "facebook";
const inst: string = "instagram";
// const x: string | null | undefined | '' = 'http:xing'
const x: string | null | undefined | "" = null;
// its horibble
const text = `
facebook = ${fb}
${x}
${x ? x : ""}
${x ? x : null}
${x && x}
${x ?? x}
instagram = ${inst}
`;
console.log(text);
# Javascript Closures
var num = 4;
function outer() {
var num = 2;
function inner() {
num++;
var num = 3;
console.log(num);
}
inner();
}
outer(); // 3
# Arrays
- How to add and remove from start and end of array?
push,pop,unshift,shift - Test if item in array
array.includes(item)
# JSON and Objects
javascript can parse JSON (string) easily, Objects require more tokenization parsing processing
# Modules System
commonJS, UMD, AMD, ES6 Modules
import * as React from "react";
const { useState } = React;
# Diff b/w == and ===
| operator | description |
|---|---|
| == | checks only values |
| === | checks both type and value |
1 == "1" ? console.log("T") : console.log("F");
1 === "1" ? console.log("T") : console.log("F");
# Variable Arguments, Parametric Polymorphism
function variableArguments(...args: any[]) {
console.log(args.length);
console.log(...args);
}
variableArguments("hello", "how", "are", "yo", 4, 3, 2);